Introduction
The sun is often seen as a source of warmth and light, offering numerous benefits like boosting mood and providing essential vitamin D. However, prolonged sun exposure without proper protection can have detrimental effects on the skin, significantly increasing the risk of skin cancer. Skin cancer is one of the most common types of cancer, and much of it is preventable with the right precautions. In this blog, we will explore how sun exposure contributes to the development of skin cancer, the importance of early detection, and the best ways to protect your skin from harmful UV rays.
What is Skin Cancer?
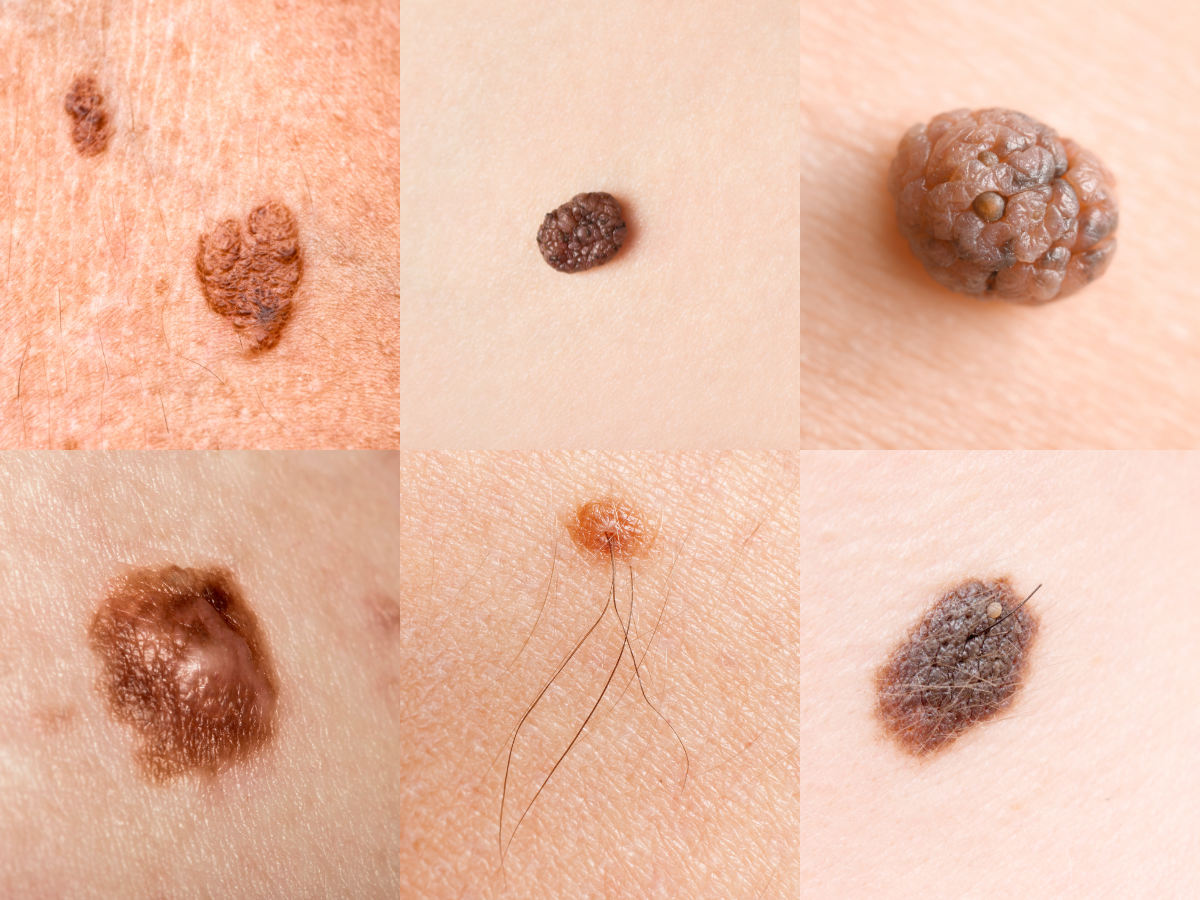
Skin cancer occurs when the skin cells begin to grow abnormally, forming tumors. The two most common types of skin cancer are non-melanoma skin cancers (including basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma) and melanoma, which is more aggressive and can spread to other parts of the body. Skin cancer is primarily caused by damage to the skin cells, often from ultraviolet (UV) radiation, which is emitted by the sun and tanning beds.
UV Radiation and Skin Damage
The sun emits three types of UV radiation: UVA, UVB, and UVC. While UVC rays are absorbed by the Earth’s atmosphere, UVA and UVB rays can penetrate the skin and cause damage:
- UVA rays: These rays penetrate deep into the skin and are primarily responsible for premature aging, wrinkles, and sunspots. They can also contribute to skin cancer by causing DNA damage in skin cells.
- UVB rays: UVB rays are the main culprits behind sunburn and are known to cause direct DNA damage. These rays are most intense during midday hours (10 a.m. to 4 p.m.) and at higher altitudes.
Excessive exposure to these rays over time can weaken the skin’s ability to repair itself, leading to mutations in skin cells that can eventually become cancerous.
Risks for Developing Skin Cancer
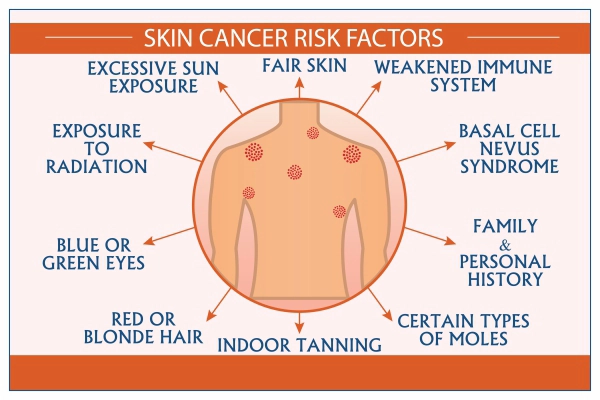
Several factors can increase your risk of developing skin cancer, most of which are related to the amount of UV radiation your skin is exposed to over time. The primary risk factor is sunburns and prolonged sun exposure without protection. If you have a history of severe sunburns, especially during childhood, your risk of skin cancer increases. Other factors include having a family history of skin cancer, fair skin, a weakened immune system, and living in areas with high sun exposure (such as near the equator or at high altitudes). People who spend significant time outdoors for work or leisure are also at higher risk, particularly if they don’t take proper sun protection measures.
UV Radiation Facts
UV radiation is a major environmental factor in the development of skin cancer. It’s important to note that UV rays can penetrate through clouds and reflect off surfaces such as water, sand, and snow, meaning you can still be exposed to harmful radiation even when you don’t feel the sun directly on your skin. UV radiation consists of three types: UVA, UVB, and UVC, with UVA and UVB being the most harmful to the skin. UVA rays penetrate deep into the skin, leading to long-term skin damage and aging, while UVB rays cause sunburn and direct DNA damage to the skin cells. UVB rays are stronger than UVA rays and play a major role in the development of skin cancer. This is why it’s essential to protect your skin from all forms of UV radiation, even on cloudy days or in winter months.
Reducing Your Risk of Skin Cancer
Reducing your risk of skin cancer requires proactive steps in minimizing UV exposure and protecting your skin. Here are some key tips for lowering your risk:
- Use Sunscreen: Apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30, and reapply every two hours. Make sure to cover all exposed areas of your skin, including ears, back of the neck, and lips.
- Wear Protective Clothing: Long sleeves, wide-brimmed hats, and sunglasses with UV protection can reduce your skin’s exposure to harmful rays.
- Seek Shade: Whenever possible, try to stay in the shade, especially during peak sunlight hours between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.
- Avoid Tanning Beds: Tanning beds expose your skin to harmful UV radiation and significantly increase your risk of skin cancer.
- Get Regular Skin Exams: Self-examine your skin regularly for any unusual moles, growths, or changes in existing moles. Professional dermatological exams should be done annually or more frequently if you’re at high risk.
Causes, Symptoms, and Risks of Skin Cancer
Causes of Skin Cancer
The leading cause of skin cancer is ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. The risk is higher in individuals who spend long periods of time outdoors without sun protection. Other factors that increase the risk of skin cancer include:
- Fair skin: Individuals with lighter skin, who burn easily, are more susceptible to UV damage.
- History of sunburns: A history of severe sunburns, especially during childhood, increases the risk of developing skin cancer later in life.
- Tanning beds: Use of artificial tanning beds exposes the skin to intense UV radiation, which can be just as harmful as the sun.
- Weakened immune system: People with compromised immune systems, such as organ transplant recipients, are more likely to develop skin cancer.
- Family history: A family history of skin cancer can increase your risk, as genetics play a significant role in determining skin sensitivity to UV damage.
Symptoms of Skin Cancer
Skin cancer can manifest in various forms, but the most common signs include:
- New growths: Unusual moles, growths, or sores that do not heal.
- Changes in existing moles: A mole that changes shape, color, or size could be a sign of melanoma.
- Itching or bleeding: Skin cancers may itch, bleed, or become painful, which is a key indicator of abnormal cell growth.
Mechanisms Leading to Skin Cancer
Skin cancer develops through a series of molecular and cellular changes caused by UV radiation exposure. UV rays damage the DNA in skin cells, causing mutations. Over time, these mutations can accumulate, disrupting the normal processes of cell growth and death. In healthy skin cells, the DNA damage is usually repaired, and the damaged cells are eliminated. However, repeated or excessive UV exposure overwhelms the body’s ability to repair this damage, allowing abnormal cells to survive and proliferate.
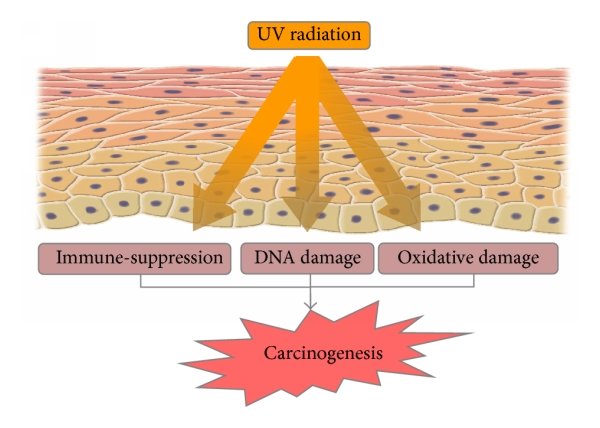
There are two main mechanisms through which UV radiation contributes to skin cancer:
- Direct DNA Damage: UVB rays directly damage the DNA in skin cells. This damage can cause mutations in critical genes that control cell growth and repair. If these mutations affect tumor suppressor genes (such as p53), the cells may begin to divide uncontrollably, leading to the formation of tumors.
- Immune System Suppression: UVA rays can suppress the immune system’s ability to detect and destroy abnormal cells. This weakens the body’s defenses against potentially cancerous cells, making it easier for them to grow and spread.
Over time, these damaged cells may evolve into non-melanoma or melanoma skin cancers, depending on the type and extent of the mutations. Preventing or minimizing UV exposure reduces the chances of these harmful processes from taking place.
By understanding these mechanisms and the risks associated with sun exposure, you can take effective steps to protect your skin and reduce your chances of developing skin cancer. Regular protection, vigilance, and skin exams are key to maintaining skin health and catching any signs of cancer early.
Treatment Options and Prevention
Treatment Options for Skin Cancer
Early detection and treatment of skin cancer are crucial in preventing its spread. The main treatment options for skin cancer include:
- Surgical Removal: This is the most common treatment, where the tumor is surgically excised from the skin.
- Mohs Surgery: For non-melanoma skin cancers, Mohs surgery allows for the precise removal of cancerous tissue while preserving as much healthy skin as possible.
- Radiation Therapy: Used for cancers that are difficult to treat with surgery, especially when they have spread.
- Topical Treatments: Some skin cancers may be treated with topical medications or creams to destroy cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: For advanced cases, chemotherapy may be necessary to treat cancer that has spread beyond the skin.
Prevention and Best Practices
Preventing skin cancer begins with understanding the risks associated with UV exposure and adopting proactive skincare habits. Here are some expert recommendations:
- Use Sunscreen: Always apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher, even on cloudy days. Reapply every two hours, and more frequently if swimming or sweating.
- Seek Shade: Avoid direct sunlight during peak hours (10 a.m. to 4 p.m.). When outdoors, try to stay under a tree or use an umbrella for shade.
- Wear Protective Clothing: Long sleeves, hats, and sunglasses can help shield your skin from harmful UV rays.
- Avoid Tanning Beds: Artificial UV radiation is just as harmful as the sun. It’s best to avoid tanning beds entirely.
- Get Regular Skin Checks: Regular self-examinations and professional check-ups can help detect skin cancer early, improving the chances of successful treatment.
Additional Tips for Healthy Skin
Protecting your skin from UV rays isn’t just about preventing skin cancer; it’s also about maintaining the overall health and appearance of your skin. To keep your skin looking youthful and healthy, consider the following tips:
- Hydration: Keep your skin hydrated by drinking plenty of water and using moisturizing products that help to lock in moisture.
- Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals can help your skin repair itself and stay healthy.
- Anti-aging Treatments: Treatments such as microdermabrasion, HydraFacials, and skin tightening lasers can rejuvenate your skin and repair the effects of sun damage.
Hospital Introduction
Skinzone Clinics in Borivali, Mumbai, is a trusted destination for advanced dermatology, aesthetic, and trichology treatments. We offer a well-rounded, evidence-based approach to skincare, combining proven technologies with personalized care. Our expert team is committed to long-term skin health, delivering transformative results through innovative procedures tailored to each individual. At Skinzone, every treatment is designed to enhance natural beauty while prioritizing safety, transparency, and effectiveness — making us a leading choice for those seeking holistic and lasting solutions.
Specializing in Medspa treatments, including HIFU, Microdermabrasion, HydraFacials, Anti-Aging, Botox, and Laser Pigmentation, Skinzone also offers expert care for various skin and hair conditions, including acne, vitiligo, and hair loss in both men and women. Contact us today for a consultation at our Borivali or Pune clinic.
Contact Details
Borivali: Office No. 403, Vini Elegance, Above Tanishq Jewellers, L.T. Road, Borivali West, Mumbai – 400092, +91 8657536730, skinzoneclinics@gmail.com
Pune: Office No. 588, B3, 1st Floor, Ganesh Market, Bibwewadi Kondhwa Rd, next to Spire Hospital, Pune – 411037, +91 9766540054, skinzoneclinics@gmail.com
FAQs
- How can I protect my skin from the sun?
Use sunscreen, wear protective clothing, and avoid peak sun hours (10 a.m. to 4 p.m.). - What are the early signs of skin cancer?
New growths, changes in existing moles, or itching and bleeding can indicate skin cancer. - Can tanning cause skin cancer?
Yes, tanning beds expose you to harmful UV rays that increase the risk of skin cancer. - Is it necessary to use sunscreen every day?
Yes, sunscreen should be used daily, even when it’s cloudy or cold. - What are the treatment options for skin cancer?
Treatment options include surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, and topical treatments depending on the type and stage of cancer.
Conclusion
Skin cancer is a serious and preventable condition, with excessive sun exposure being one of the leading causes. By protecting your skin, seeking regular check-ups, and adopting healthy skincare habits, you can significantly reduce your risk. If you suspect any signs of skin cancer, consulting a dermatologist promptly can help ensure early detection and effective treatment. Protect your skin today for a healthier tomorrow!