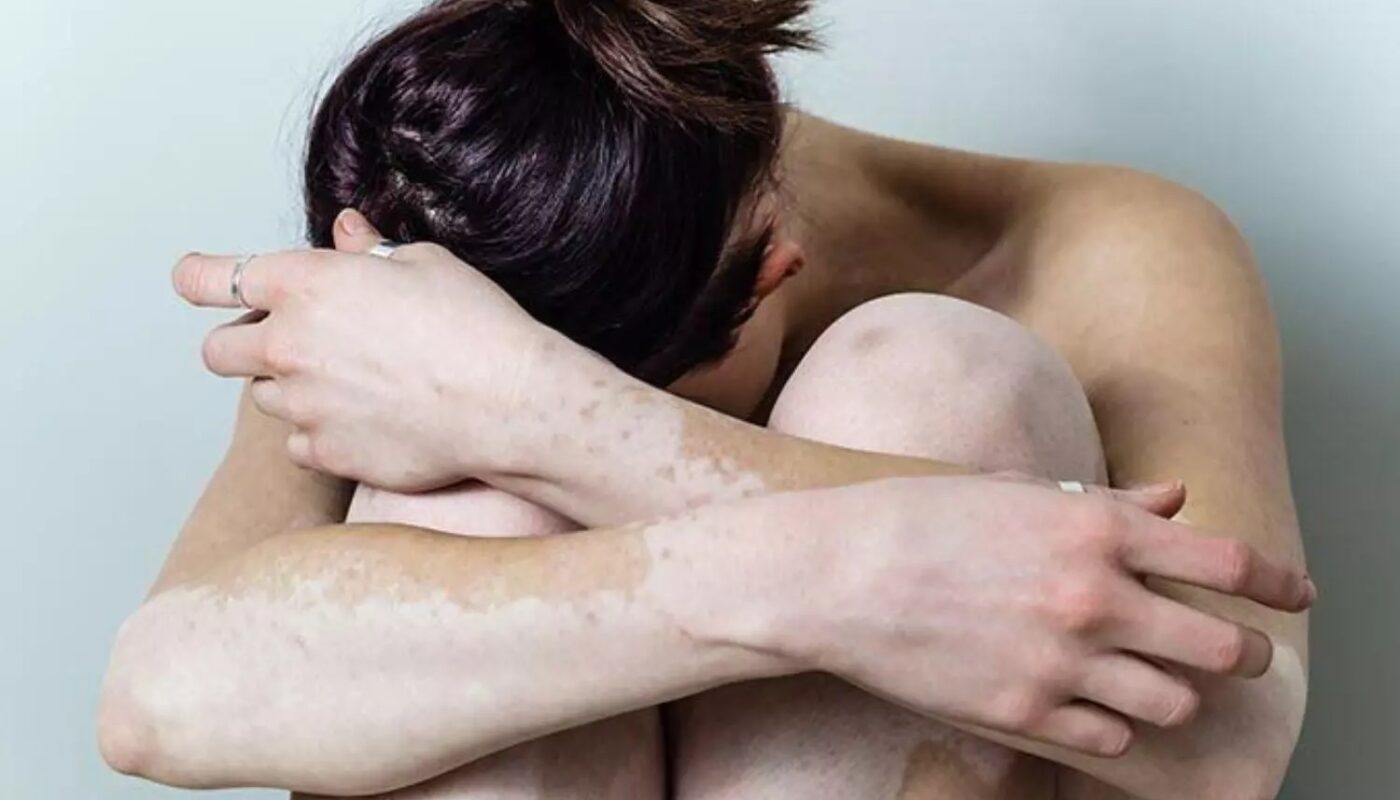
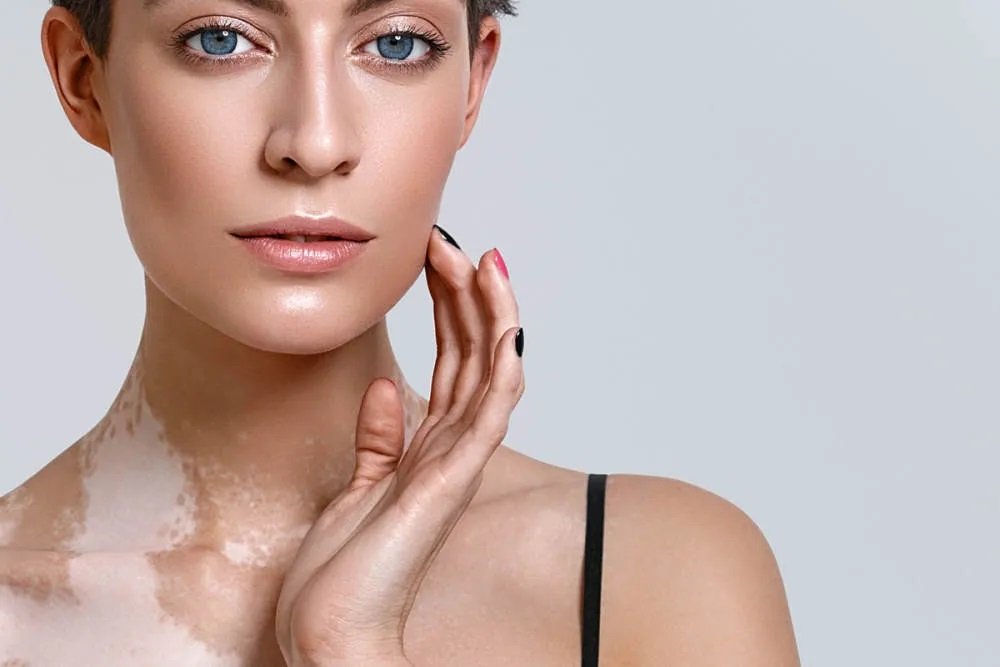
Vitiligo is a chronic skin condition characterized by the loss of pigment, resulting in white patches on the skin. It affects people of all ages, genders, and ethnic backgrounds. Although vitiligo is not life-threatening or contagious, it can significantly impact an individual’s self-esteem and quality of life. In this blog, we will delve into the symptoms, causes, types, and risk factors associated with vitiligo.
Symptoms of Vitiligo
Skin
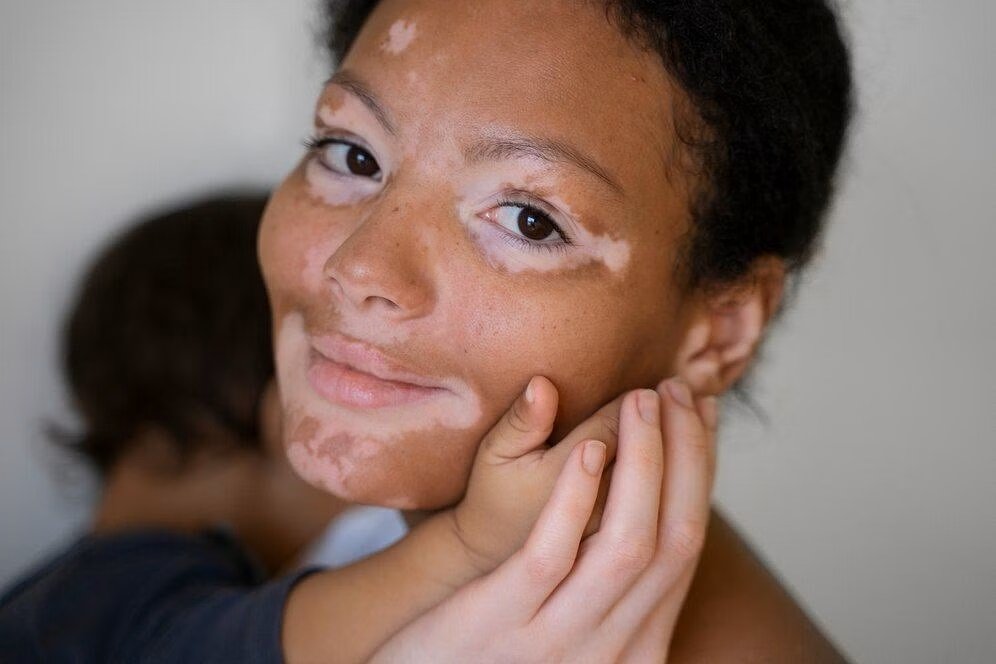

- Patches often first appear on sun-exposed areas, like the hands, feet, arms, face, and lips.
Hair
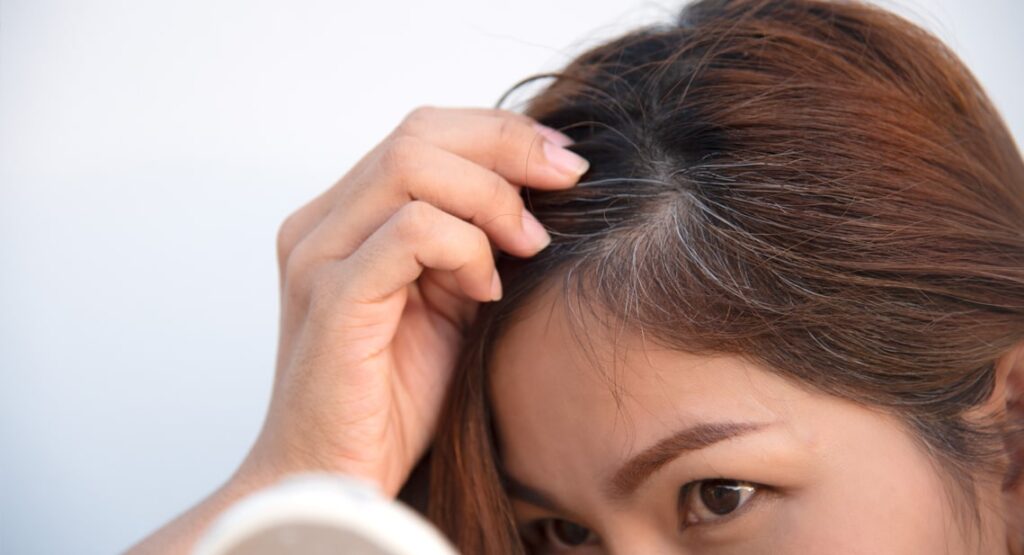

- Premature graying or whitening of hair on the scalp, eyebrows, eyelashes, or beard.
Mucous Membranes
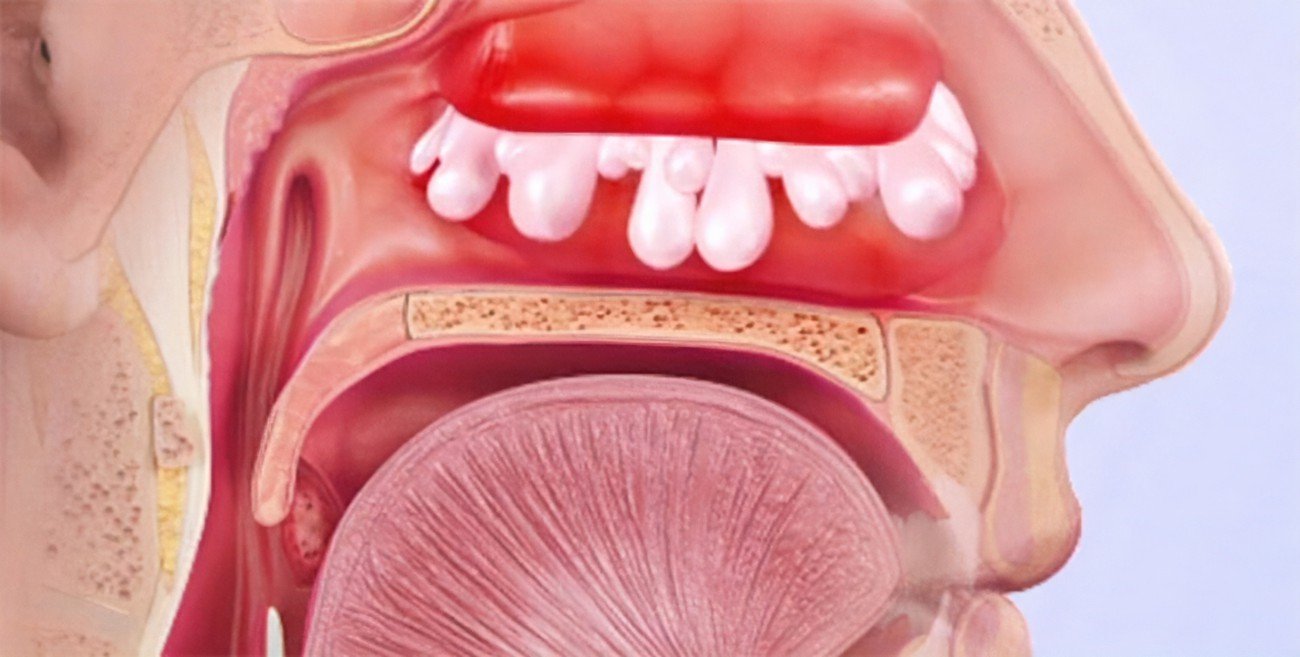
- Loss of color inside the mouth and nose.
Eyes
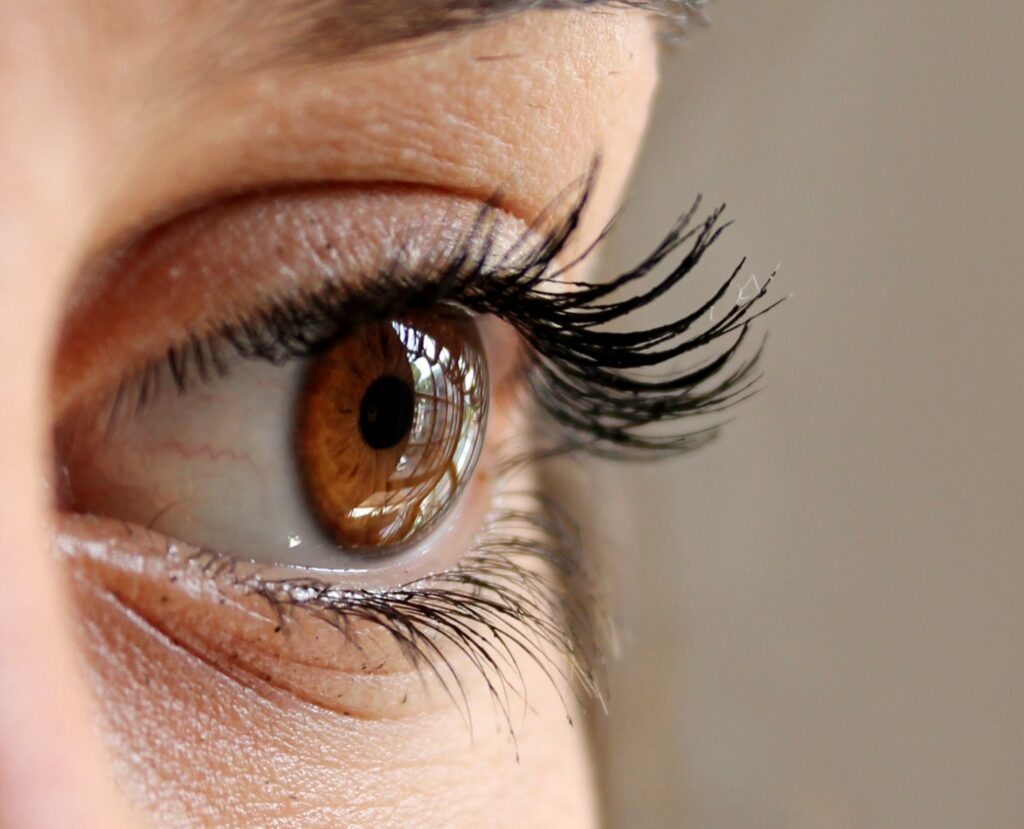
- Change in color of the retina.
The extent and rate of pigmentation from vitiligo are unpredictable. The condition can simultaneously affect many parts of the body (generalized vitiligo), only one side or part of the body (segmental vitiligo), or a few areas of the body (localized or focal vitiligo).
Causes of Vitiligo
Genetics

- There is a higher likelihood of developing vitiligo if there is a family history of the disorder.
Autoimmune Diseases
- People with autoimmune diseases like hyperthyroidism, alopecia aerate, and pernicious anemia are at increased risk.

Environmental Triggers

- Exposure to certain chemicals or significant stress may trigger vitiligo in genetically predisposed individuals.
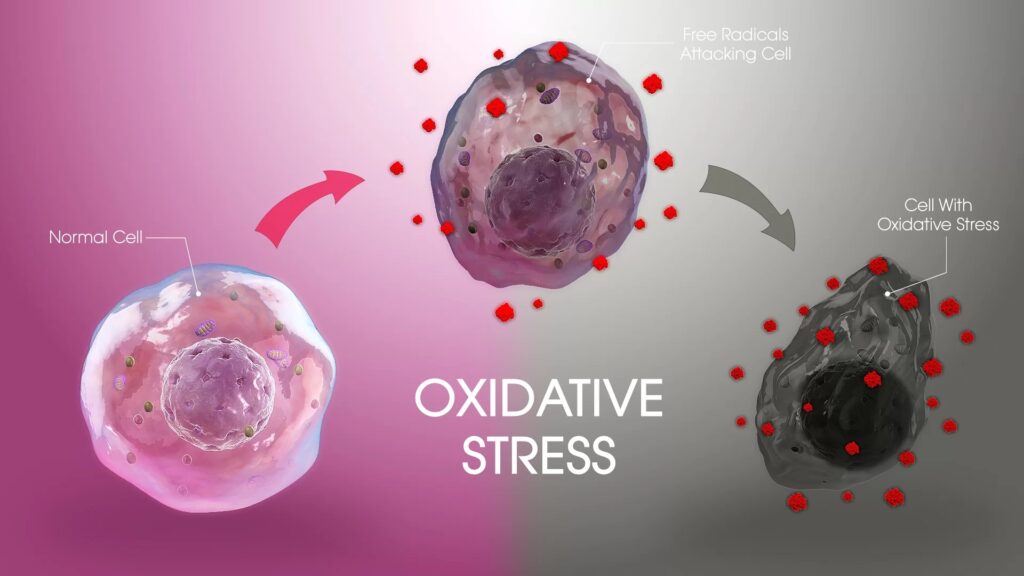
Oxidative Stress
- An imbalance between antioxidants and free-radicals in the body might lead to the destruction of melanocytes.
Types of Vitiligo
Vitiligo is classified into several types based on the pattern and extent of depigmentation:
Generalized Vitiligo
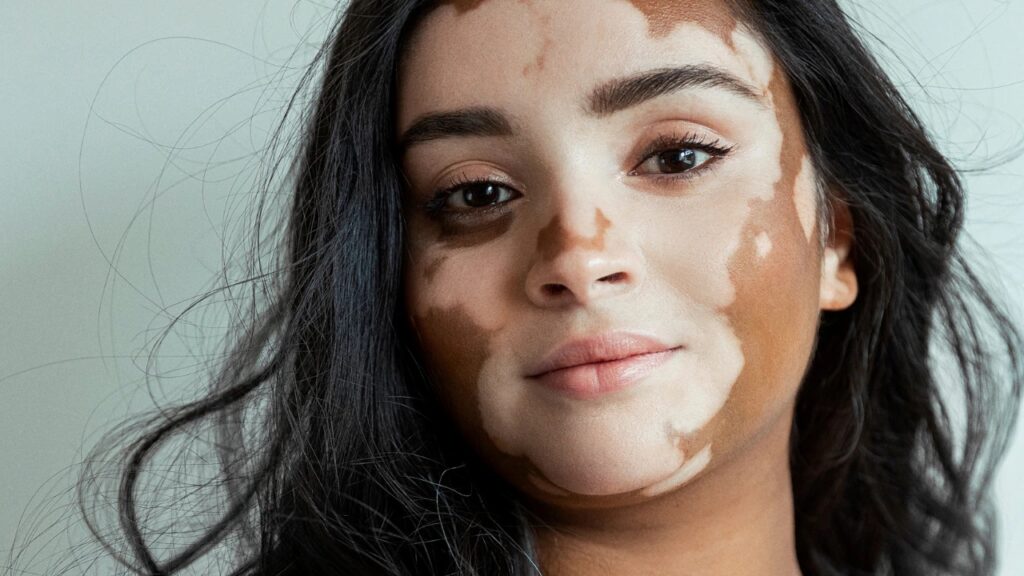

- The most common type, where depigmented patches are distributed symmetrically across various parts of the body.
Segmental Vitiligo
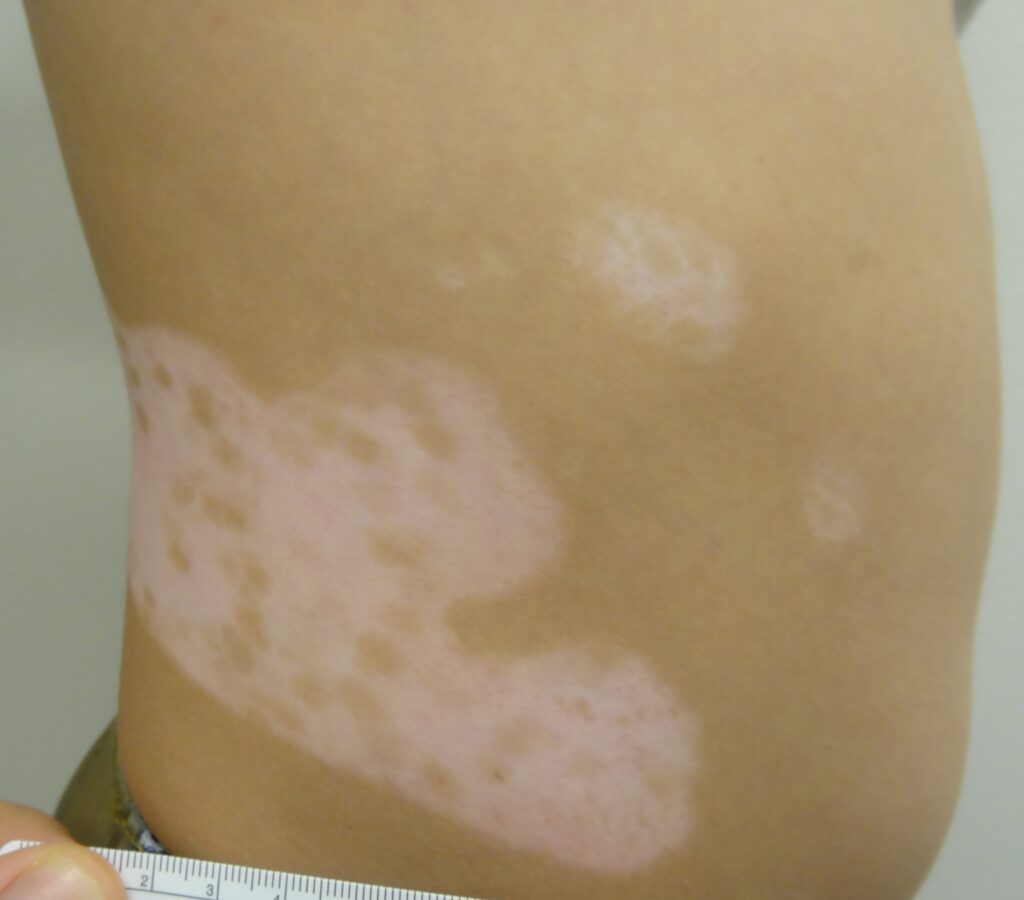
- A less common type, where patches appear on one segment or side of the body.
- It typically starts at a younger age and progresses for a few years before stabilizing.
Focal Vitiligo
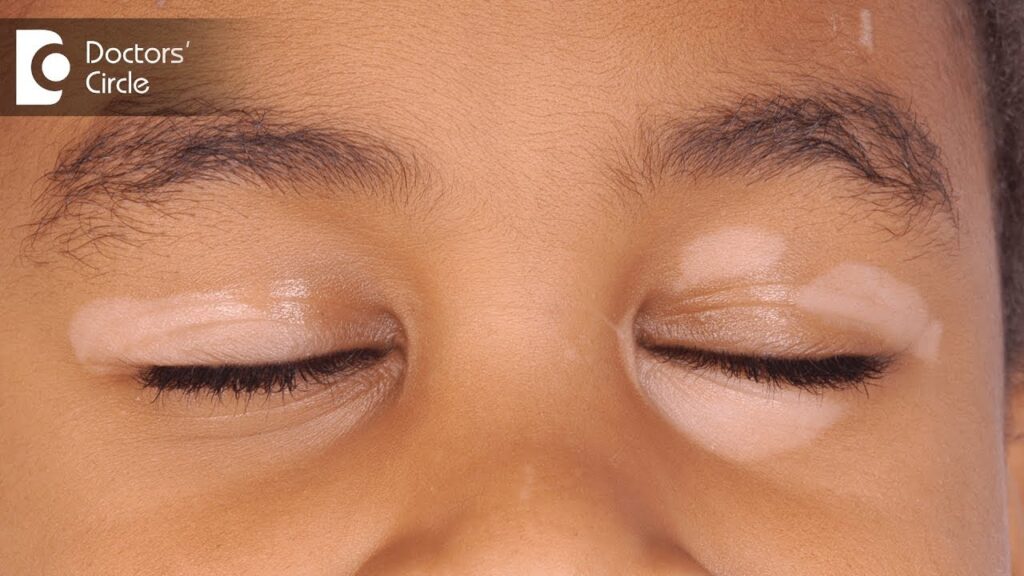
- Characterized by one or a few scattered white patches in a localized area.
Acrofacial Vitiligo
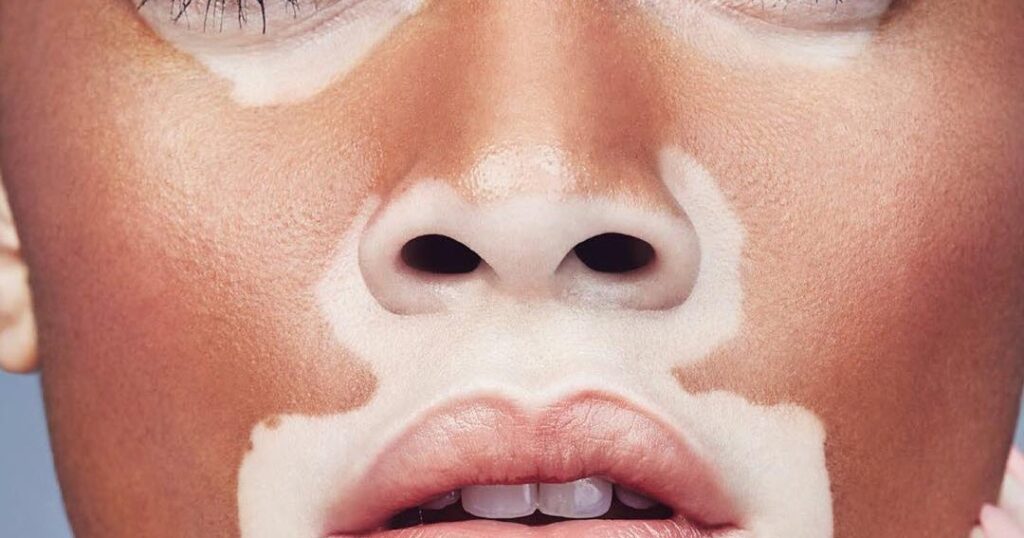

- Depigmentation occurs on the fingers and toes, and around facial orifices such as the eyes, nose, and mouth.
Mucosal Vitiligo

- This form of vitiligo affects the mucous membranes of the mouth or genitals.
Risk Factors for Vitiligo
While the precise cause of vitiligo remains unclear, certain factors increase the chances of developing vitiligo:
Family History
- Having a close relative with vitiligo or other autoimmune diseases increases the risk.

Autoimmune Disorders
- Individuals with autoimmune diseases are more susceptible to developing vitiligo.
Genetics
- Specific genes associated with immune regulation and skin pigmentation may predispose individuals to vitiligo.

Environmental Factors
- Exposure to certain chemicals, sunburn, or severe emotional stress can act as triggers.
Conclusion
Vitiligo is a complex condition with various causes and manifestations. Understanding the symptoms, types, and risk factors is crucial for early diagnosis and management. While there is no cure for vitiligo, treatments such as topical corticosteroids, phototherapy, and skin grafts can help manage the condition and improve the look of affected skin. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of vitiligo, it is essential to consult a dermatologist for a detailed evaluation and personalized treatment plan.
Remember, living with vitiligo can be very challenging, but with the right support and care, people can lead fulfilling lives and embrace their unique beauty.